Identify the tissue depicted in the photomicrograph. – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of histology, where we unravel the secrets of tissues, the fundamental building blocks of life. By deciphering the intricacies of cellular architecture and organization, we unlock the mysteries of tissue function and delve into the fascinating relationship between structure and function.
Prepare to be enthralled as we embark on this exploration, armed with the tools of microscopy and the boundless curiosity of scientific inquiry.
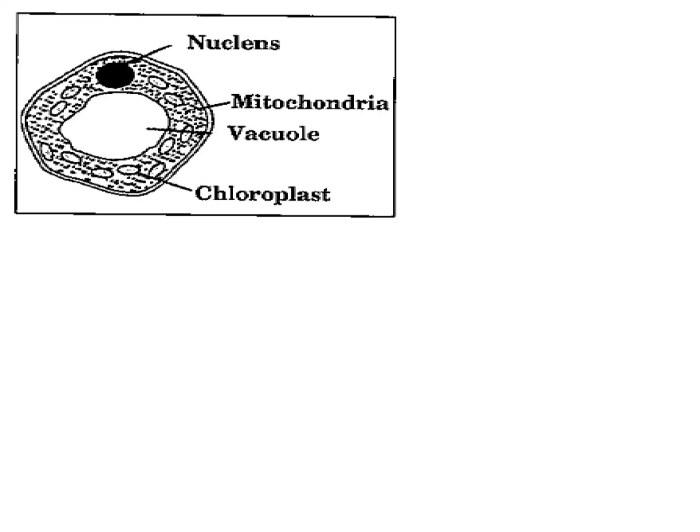
Tissue Classification

Tissues are groups of cells with similar structure and function. They can be classified into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
Epithelial tissuecovers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body. It is composed of closely packed cells that form a protective barrier.
Connective tissuesupports and connects other tissues. It is composed of cells that are separated by a large amount of extracellular matrix.
Muscle tissueis responsible for movement. It is composed of cells that contain specialized proteins that allow them to contract.
Nervous tissueis responsible for communication and control. It is composed of cells that are specialized for the transmission of electrical signals.
Tissue Organization
The arrangement of cells and extracellular matrix in a tissue is known as its organization. The organization of a tissue is related to its function.
For example, epithelial tissue is typically organized into a single layer of cells that covers a surface. This organization allows epithelial tissue to form a protective barrier.
Connective tissue is typically organized into a loose network of cells that are separated by a large amount of extracellular matrix. This organization allows connective tissue to support and connect other tissues.
Muscle tissue is typically organized into bundles of cells that are arranged in a parallel fashion. This organization allows muscle tissue to contract.
Nervous tissue is typically organized into networks of cells that are connected by synapses. This organization allows nervous tissue to transmit electrical signals.
Cell Morphology
The shape, size, and organelles of cells in a tissue are known as its morphology. The morphology of cells is related to their function.
For example, epithelial cells are typically thin and flat. This shape allows them to form a close-fitting barrier.
Connective tissue cells are typically irregular in shape. This shape allows them to fill in the spaces between other tissues.
Muscle cells are typically long and thin. This shape allows them to contract.
Nervous tissue cells are typically branched. This shape allows them to form connections with other cells.
Extracellular Matrix, Identify the tissue depicted in the photomicrograph.
The extracellular matrix is a complex network of proteins and polysaccharides that surrounds cells in a tissue. The extracellular matrix provides support and protection for cells, and it also plays a role in cell communication.
The composition of the extracellular matrix varies depending on the type of tissue. For example, the extracellular matrix of connective tissue is composed of collagen and elastin. The extracellular matrix of epithelial tissue is composed of a basement membrane.
The extracellular matrix contributes to the function of a tissue. For example, the extracellular matrix of connective tissue provides support for the cells of the tissue. The extracellular matrix of epithelial tissue provides a barrier to protect the cells of the tissue.
Tissue Function
The function of a tissue is determined by the structure and organization of its cells and extracellular matrix.
For example, epithelial tissue functions to protect the body from the environment. Connective tissue functions to support and connect other tissues. Muscle tissue functions to produce movement. Nervous tissue functions to transmit electrical signals.
Tissue Location
The location of a tissue in the body is related to its function.
For example, epithelial tissue is found on the surfaces of the body and lining the cavities of the body. Connective tissue is found throughout the body, supporting and connecting other tissues. Muscle tissue is found in muscles, which are responsible for movement.
Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, which are responsible for communication and control.
Questions Often Asked: Identify The Tissue Depicted In The Photomicrograph.
What is the significance of tissue classification?
Tissue classification provides a systematic framework for understanding the diverse range of tissues in the body, enabling researchers and medical professionals to study and compare their structure, function, and development.
How does the extracellular matrix contribute to tissue function?
The extracellular matrix serves as a dynamic scaffold, providing structural support, regulating cell behavior, and facilitating intercellular communication, ultimately influencing tissue function and integrity.
What are the key features of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is characterized by closely packed cells that form continuous sheets, creating a barrier or lining that protects underlying tissues and regulates the passage of substances.