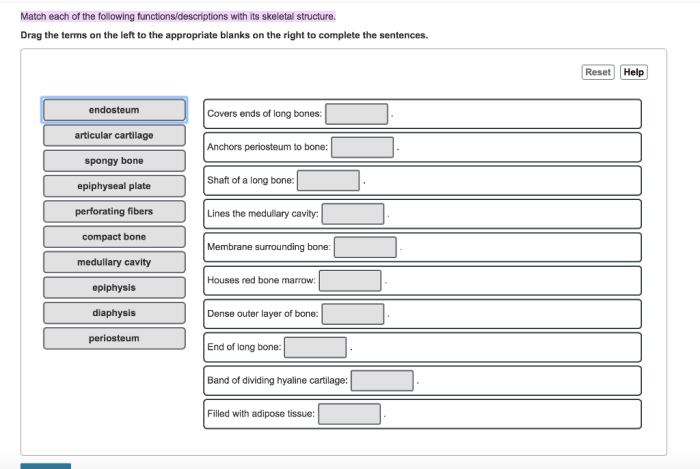
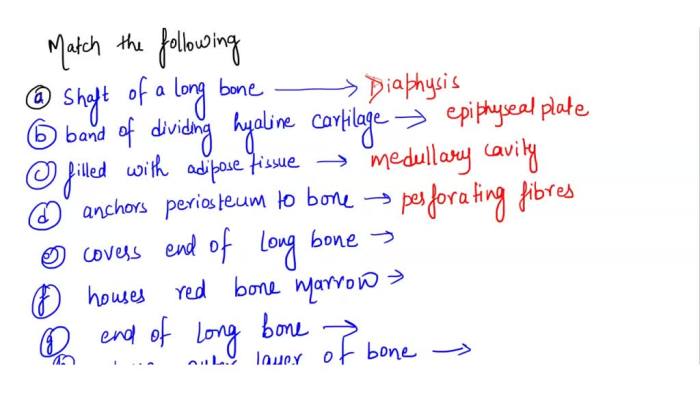
Match each of the following functions/descriptions with its skeletal structure. The skeletal system, a remarkable framework within our bodies, plays a multifaceted role in maintaining our physical well-being. From providing structural support to facilitating movement, the skeletal system’s diverse functions are intricately linked to its unique structures.
This guide delves into the intricate relationship between skeletal functions and their corresponding structures, offering a comprehensive understanding of this vital system.
As we explore the skeletal system’s functions, we will uncover the mechanisms behind its remarkable abilities. We will delve into the distinct characteristics of each skeletal structure, examining how they enable the skeletal system to fulfill its essential roles. Through real-world examples, we will witness the practical applications of these functions, solidifying our understanding of the skeletal system’s significance.
Functions of Skeletal System: Match Each Of The Following Functions/descriptions With Its Skeletal Structure

The skeletal system plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure, movement, and overall health of the body. Its primary functions include:
- Support:The skeletal framework provides support to the body, allowing it to stand upright and perform various movements.
- Protection:The bones of the skull, rib cage, and pelvis protect vital organs from external forces and injuries.
- Movement:Muscles attach to bones, enabling them to move and perform various actions, such as walking, running, and grasping objects.
- Mineral Storage:The bones act as reservoirs for minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for maintaining bone strength and overall health.
- Blood Cell Production:The bone marrow, found within certain bones, produces red and white blood cells, which are essential for oxygen transport and immune function.
Skeletal Structures
The skeletal system consists of different types of skeletal structures, each with unique characteristics:
- Long Bones:These are long, cylindrical bones found in the limbs (arms and legs) and provide support and mobility.
- Short Bones:These are small, cube-shaped bones found in the wrists and ankles and provide stability.
- Flat Bones:These are thin, plate-like bones found in the skull, rib cage, and pelvis and provide protection and support.
- Irregular Bones:These have complex shapes and are found in the spine, skull, and facial bones and provide protection and support.
- Sesamoid Bones:These are small, round bones embedded in tendons and help reduce friction and protect tendons.
Matching Functions to Structures
| Functions of Skeletal System | Long Bones | Short Bones | Flat Bones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Protection | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Movement | ✓ | ||
| Mineral Storage | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Blood Cell Production |
Examples of Skeletal Functions and Structures
- The long bones of the legs support the body’s weight and enable walking and running.
- The flat bones of the skull protect the brain from external forces.
- The short bones of the wrist provide stability to the hand and enable precise movements.
- The sesamoid bone in the knee, known as the patella, protects the knee joint and facilitates movement.
- The bone marrow within long bones produces red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
FAQ Guide
What are the primary functions of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system provides structural support, facilitates movement, protects vital organs, produces blood cells, and stores minerals.
How many types of skeletal structures are there?
There are three main types of skeletal structures: axial, appendicular, and splanchnic.
What is the function of the axial skeleton?
The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body and includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.