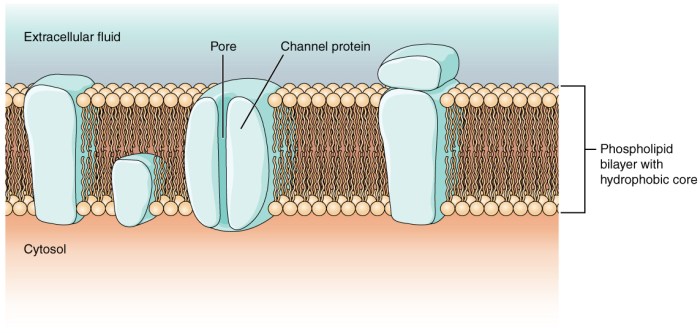
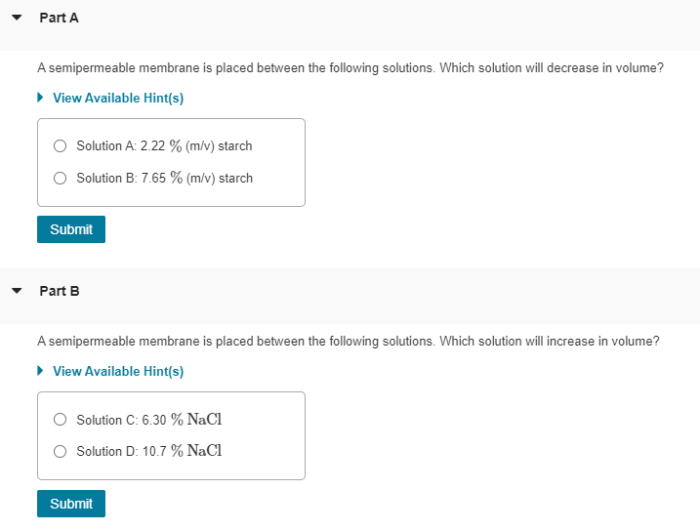
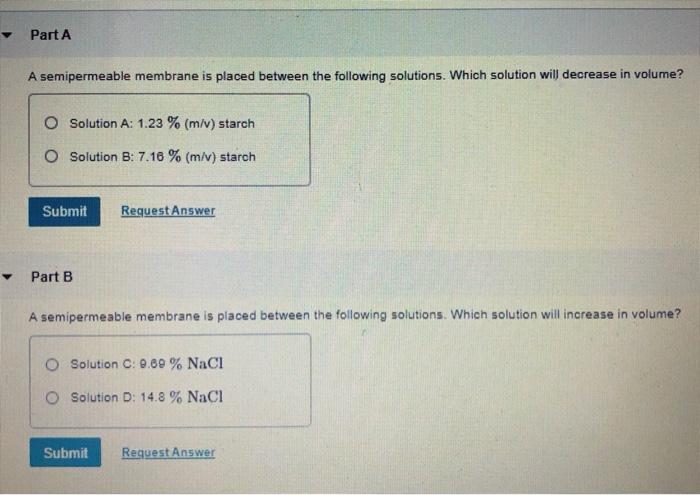
A semipermeable membrane is placed between the following solutions – When a semipermeable membrane is placed between different solutions, it creates a fascinating scenario that unveils the intricacies of osmosis and its profound impact on various biological and industrial processes. This membrane acts as a selective barrier, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting others, leading to a dynamic exchange of water and solutes across its boundaries.
Osmosis, driven by concentration gradients, governs the movement of water molecules across the semipermeable membrane. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating fluid balance, and facilitating nutrient transport in living organisms. Understanding the principles of osmosis and the applications of semipermeable membranes is essential for comprehending a wide range of scientific and technological advancements.
Solutions and Semipermeable Membranes
A semipermeable membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while blocking others. In the context of osmosis, a semipermeable membrane separates two solutions with different concentrations of solutes.
Solutions can be classified based on their solute concentration relative to another solution:
- Hypotonic solution:A solution with a lower solute concentration than another solution.
- Hypertonic solution:A solution with a higher solute concentration than another solution.
- Isotonic solution:A solution with the same solute concentration as another solution.
Osmosis and Diffusion
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
Osmosis occurs because water molecules are constantly moving in random directions. When there is a difference in solute concentration across a membrane, the water molecules will move towards the side with the higher solute concentration in an attempt to dilute it.
Diffusion, A semipermeable membrane is placed between the following solutions
Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
In the context of osmosis, diffusion plays a role in the movement of solutes across the semipermeable membrane. Solutes will diffuse from the side with the higher concentration to the side with the lower concentration, until equilibrium is reached.
Water Movement and Concentration Changes
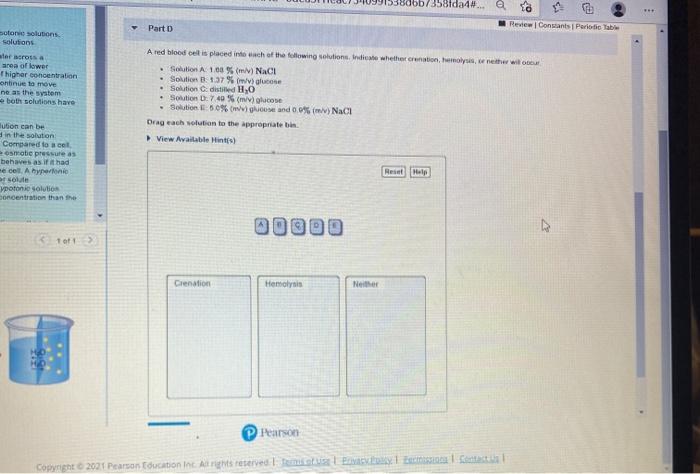
When a semipermeable membrane separates two solutions of different concentrations, water molecules will move across the membrane to equalize the solute concentrations on both sides.
In a hypotonic solution, there is a higher concentration of water molecules outside the cell compared to inside. This causes water to move into the cell, resulting in an increase in cell volume.
In a hypertonic solution, there is a higher concentration of water molecules inside the cell compared to outside. This causes water to move out of the cell, resulting in a decrease in cell volume.
In an isotonic solution, the concentration of water molecules is the same on both sides of the membrane, so there is no net movement of water.
Applications of Semipermeable Membranes
Semipermeable membranes have a wide range of applications in various fields:
- Water purification:Semipermeable membranes are used in reverse osmosis systems to remove impurities from water.
- Medical devices:Semipermeable membranes are used in dialysis machines to remove waste products from the blood.
- Food processing:Semipermeable membranes are used in ultrafiltration and microfiltration processes to separate and purify food products.
Factors Affecting Osmosis
The rate and direction of osmosis can be affected by several factors:
- Temperature:The rate of osmosis increases with temperature.
- Membrane thickness:The thicker the membrane, the slower the rate of osmosis.
- Surface area:The larger the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of osmosis.
- Membrane selectivity:The selectivity of the membrane for certain molecules or ions can affect the rate of osmosis.
- Solute size:The size of the solute molecules can affect the rate of osmosis.
Essential FAQs: A Semipermeable Membrane Is Placed Between The Following Solutions
What is the role of a semipermeable membrane in osmosis?
A semipermeable membrane acts as a selective barrier, allowing water molecules to pass through while restricting the passage of solutes. This differential permeability creates a concentration gradient across the membrane, driving the movement of water molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
How does osmosis affect living organisms?
Osmosis plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating fluid balance in living organisms. For example, in plant cells, osmosis helps maintain cell turgidity, while in red blood cells, it prevents hemolysis by regulating water movement across the cell membrane.
What are some practical applications of semipermeable membranes?
Semipermeable membranes have numerous practical applications, including water purification, medical devices (e.g., dialysis and artificial kidneys), and industrial processes (e.g., reverse osmosis for desalination).