Quentin made a table to summarize uses of electromagnetic waves – Quentin’s meticulously crafted table unveils the multifaceted uses of electromagnetic waves, offering a comprehensive overview of their transformative impact across diverse fields. From communication to medicine and technology, electromagnetic waves have revolutionized our understanding of the world and continue to shape our daily lives.
This exploration delves into the types of electromagnetic waves, their unique properties, and the electromagnetic spectrum’s organization. We examine how these waves interact with matter and explore their practical applications in everyday devices and scientific advancements.
Uses of Electromagnetic Waves: Quentin Made A Table To Summarize Uses Of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are an essential part of our modern world. They are used in a wide variety of applications, from communication to medicine to scientific research.
One of the most important uses of electromagnetic waves is in communication. Electromagnetic waves can be used to transmit information over long distances, making them ideal for use in telephones, radios, and televisions. They are also used in wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
Electromagnetic waves are also used in medicine. They can be used to create images of the inside of the body, which can help doctors to diagnose and treat diseases. Electromagnetic waves are also used in cancer treatment, such as radiation therapy.
In addition to communication and medicine, electromagnetic waves are also used in a variety of other applications, such as:
- Technology: Electromagnetic waves are used in a wide variety of technologies, such as computers, microwaves, and radar.
- Scientific research: Electromagnetic waves are used in a variety of scientific research, such as astronomy and particle physics.
- Exploration: Electromagnetic waves are used in a variety of exploration, such as remote sensing and space exploration.
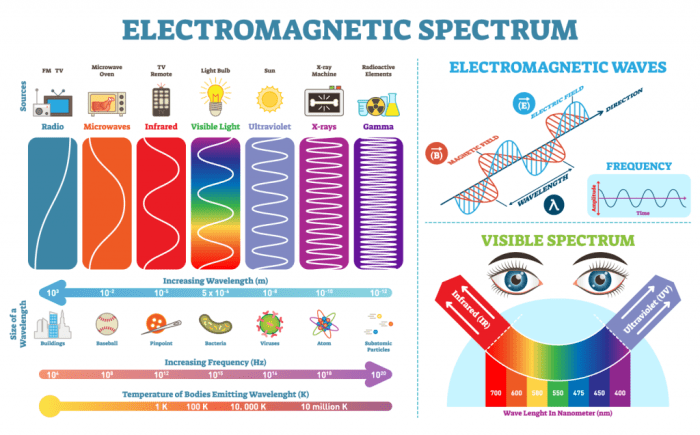
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
There are many different types of electromagnetic waves, each with its own unique properties. The different types of electromagnetic waves are classified according to their frequency and wavelength.
The following table summarizes the different types of electromagnetic waves, their frequencies, and their applications:
| Type of Electromagnetic Wave | Frequency Range | Wavelength Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio waves | 3 Hz to 300 GHz | 100 km to 1 mm | Communication, navigation, radar |
| Microwaves | 300 MHz to 300 GHz | 1 m to 1 mm | Cooking, heating, communication |
| Infrared radiation | 300 GHz to 400 THz | 1 mm to 700 nm | Heating, night vision, remote controls |
| Visible light | 400 THz to 790 THz | 700 nm to 400 nm | Seeing, photography, communication |
| Ultraviolet radiation | 790 THz to 30 PHz | 400 nm to 10 nm | Sunbathing, disinfection, cancer treatment |
| X-rays | 30 PHz to 30 EHz | 10 nm to 0.01 nm | Medical imaging, security, industrial inspection |
| Gamma rays | 30 EHz to 300 EHz | 0.01 nm to 0.0001 nm | Cancer treatment, nuclear physics, astronomy |
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves have a number of fundamental properties, including their speed, wavelength, and frequency.
The speed of electromagnetic waves is the same in all inertial frames of reference, and is equal to the speed of light, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second).
The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave. The wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency of the wave, meaning that waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is the number of peaks or troughs that pass a given point in one second. The frequency is directly proportional to the energy of the wave, meaning that waves with higher frequencies have higher energies.
These properties of electromagnetic waves affect their behavior and applications. For example, the speed of electromagnetic waves makes them ideal for use in communication, as they can be used to transmit information over long distances quickly and efficiently. The wavelength of electromagnetic waves determines their ability to penetrate different materials, making them useful for a variety of applications, such as medical imaging and security.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
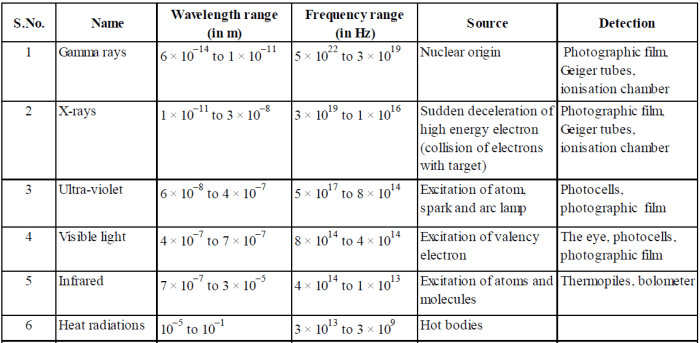
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is divided into seven regions, each with its own unique properties and applications.
The following table summarizes the different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, their frequencies, and their uses:
| Region of the Electromagnetic Spectrum | Frequency Range | Wavelength Range | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio waves | 3 Hz to 300 GHz | 100 km to 1 mm | Communication, navigation, radar |
| Microwaves | 300 MHz to 300 GHz | 1 m to 1 mm | Cooking, heating, communication |
| Infrared radiation | 300 GHz to 400 THz | 1 mm to 700 nm | Heating, night vision, remote controls |
| Visible light | 400 THz to 790 THz | 700 nm to 400 nm | Seeing, photography, communication |
| Ultraviolet radiation | 790 THz to 30 PHz | 400 nm to 10 nm | Sunbathing, disinfection, cancer treatment |
| X-rays | 30 PHz to 30 EHz | 10 nm to 0.01 nm | Medical imaging, security, industrial inspection |
| Gamma rays | 30 EHz to 300 EHz | 0.01 nm to 0.0001 nm | Cancer treatment, nuclear physics, astronomy |
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves in Daily Life
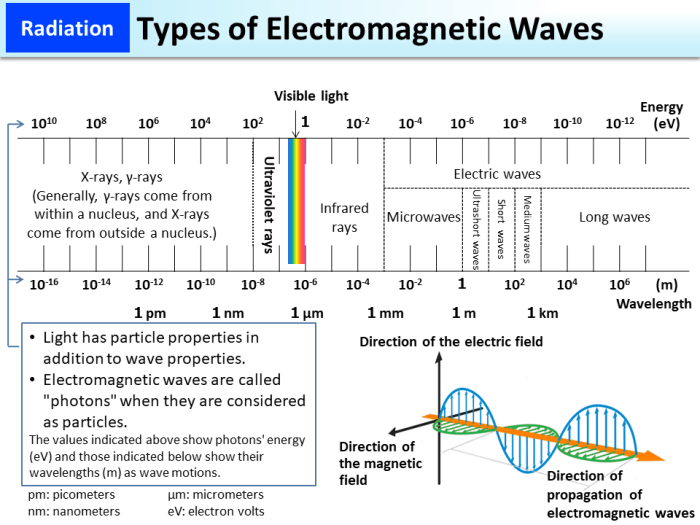
Electromagnetic waves are used in a wide variety of applications in daily life. Some of the most common applications include:
- Smartphones: Smartphones use electromagnetic waves to communicate with cell towers, allowing us to make phone calls, send text messages, and access the internet.
- Microwaves: Microwaves use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly and efficiently.
- Medical imaging equipment: Medical imaging equipment, such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners, use electromagnetic waves to create images of the inside of the body.
- Radar: Radar uses electromagnetic waves to detect objects, such as aircraft and ships.
- GPS: GPS uses electromagnetic waves to determine the location of a receiver.
These are just a few of the many applications of electromagnetic waves in daily life. Electromagnetic waves have transformed various aspects of modern society, making it possible to communicate, navigate, and access information in ways that were once impossible.
FAQ Corner
What are the main types of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are classified into various types based on their frequency and wavelength, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
How are electromagnetic waves used in communication?
Electromagnetic waves are essential for wireless communication technologies such as mobile phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication, enabling the transmission of information over long distances.
What are the medical applications of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are widely used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, providing valuable insights into the human body for diagnostic and treatment purposes.